Upgrade to Fusion part 1: Preparing to upgrade
Introduction
The dbt Fusion Engine represents the next evolution of data transformation. dbt has been rebuilt from the ground up but at its most basic, Fusion is a new version, and like any new version you should take steps to prepare to upgrade. This guide will take you through those preparations.
If Fusion is brand new to you, take a look at our comprehensive documentation on what it is, how it behaves, and what's different from dbt Core before getting started with this guide. Once you're caught up, it's time to begin preparing your projects for the speed and power that Fusion has to offer.
Prerequisites
This guide will cover the preparations for upgrading to the dbt Fusion Engine and is intended for customers already using the dbt platform with a version of dbt Core. If you're brand new to dbt, check out our quickstart guides.
To follow the steps in this guide, you must meet the following prerequisites:
- You're using a dbt platform account on any tier.
- You have a developer license.
- You have proper permissions to edit projects.
- While not a strict requirement, it's strongly recommended you focus on a project using a Fusion supported adapter:
If you have multiple dbt projects you want to upgrade to Fusion , start with smaller, newer, or more familiar projects first. This makes it easier to identify and troubleshoot any issues before upgrading larger, more complex projects.
Upgrade to the latest dbt version
Before upgrading to Fusion, you need to move your environments to the Latest release track. The Latest track includes all the features and tooling to help you prepare for Fusion, and ensures the smoothest upgrade experience by validating that your project doesn't rely on deprecated behaviors.
Always test version upgrades in development first. Use the Override dbt version feature to safely try the Latest release track without affecting your team or production runs.
Step 1: Test in development (using override)
Test the Latest release track for your individual account without changing the environment for your entire team:
- Click your account name in the left sidebar and select Account settings.
- Select Credentials from the sidebar and choose your project.
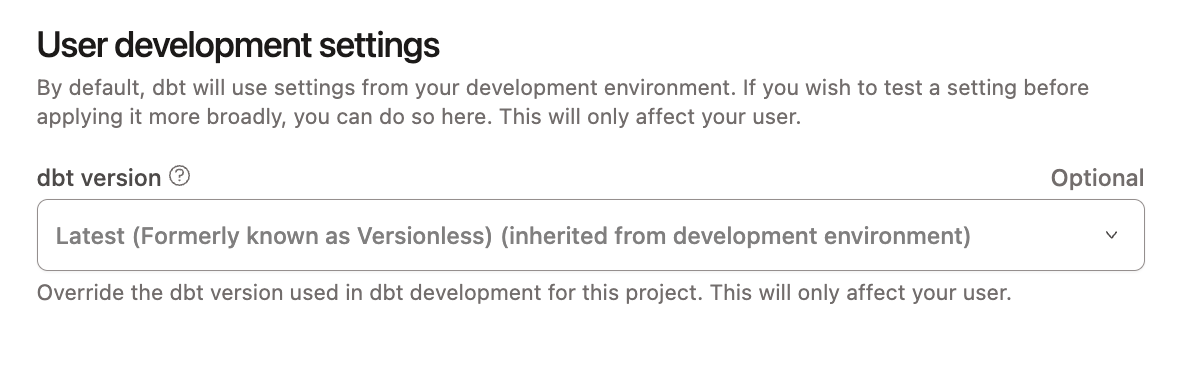
- In the side panel, click Edit and scroll to User development settings.
- Select Latest from the dbt version dropdown and click Save.
- Launch the Studio IDE or Cloud CLI and test your normal development workflows.
- Verify the override is active by running any dbt command and checking the System Logs — the first line should show
Running with dbt=and your selected version. If the version number isv1.11or higher, you're on the right path to Fusion readiness.
If everything works as expected, proceed to upgrade your environments. If you encounter deprecation warnings, don't fear! We're going to address those later in this guide. If you encounter errors, revert to your previous version and refer to the version upgrade guides to resolve any differences between your current version and the latest available dbt Core version.
Step 2: Upgrade your development environment
After successfully testing with the override, upgrade the development environment for your entire team (be sure to give them notice!):
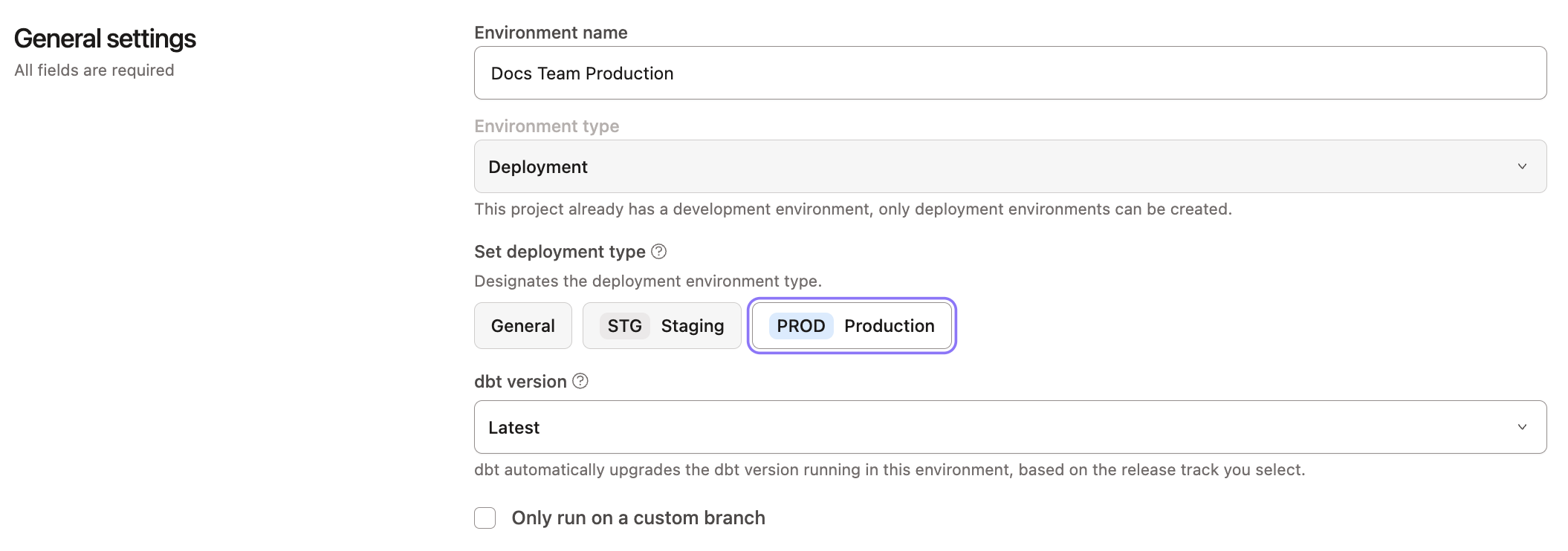
- Navigate to Environments in your project settings.
- Select your Development environment and click Edit.
- Click the dbt version dropdown and select Latest.
- Click Save to apply the changes.
Once your development environment is upgraded, you can remove your personal override by returning to your account credentials and selecting the same version as your environment.
Step 3: Upgrade staging and pre-production
If your organization has staging or pre-production environments, upgrade these before production:
- Navigate to Environments and select your staging/pre-production environment.
- Click Edit and select Latest from the dbt version dropdown.
- Click Save.
- Run your jobs in this environment for a few days to validate everything works correctly.
This provides a final validation layer before upgrading production environments.
Step 4: Upgrade your production environment
After validating in staging (or development if you don't have staging), upgrade your production environment:
- Navigate to Environments and select your Production environment.
- Click Edit and select Latest from the dbt version dropdown.
- Click Save to apply the changes.
- Monitor your first few production runs to ensure everything executes successfully.
Step 5: Update jobs
While environments control the dbt version for most scenarios, some older job configurations may have version overrides. Review your jobs and update any that specify a dbt version to ensure they use the environment's Latest release track.
Resolve all deprecation warnings
Fusion enforces strict validation and won't accept deprecated code that currently generates warnings in dbt Core. You must resolve all deprecation warnings before upgrading to Fusion. Fortunately, the autofix tool in the Studio IDE can automatically resolve most common deprecations for you.
This guide provides steps to resolve deprecation warnings without leaving dbt platform. If you prefer to work in the VS Code or Cursor editors locally, you can run the autofix in our dbt VS Code extension. Check out the installation guide for more information about those workflows.
What the autofix tool handles
The autofix tool can resolve many deprecations automatically, including:
- Moving custom configurations into the
metadictionary - Fixing duplicate YAML keys
- Correcting unrecognized resource properties
- Updating deprecated configuration patterns
Check out our deprecation references for a complete list.
Step 1: Create a new branch
Before running the autofix tool, create a new branch to isolate your changes:
- Navigate to the Studio IDE by clicking Studio in the left-side menu.
- Click the Version control panel (git branch icon) on the left sidebar.
- Click Create branch and name it something descriptive like
fusion-deprecation-fixes. - Click Create to switch to your new branch.
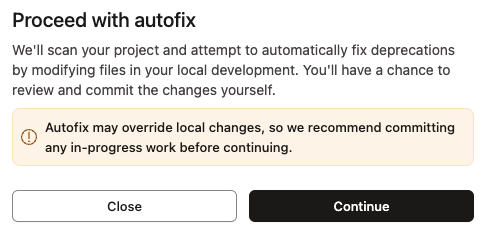
The autofix tool will modify files in your project. Make sure to commit or stash any unsaved work to avoid losing changes.
Step 2: Run the autofix tool
Now you're ready to scan for and automatically fix deprecation warnings:
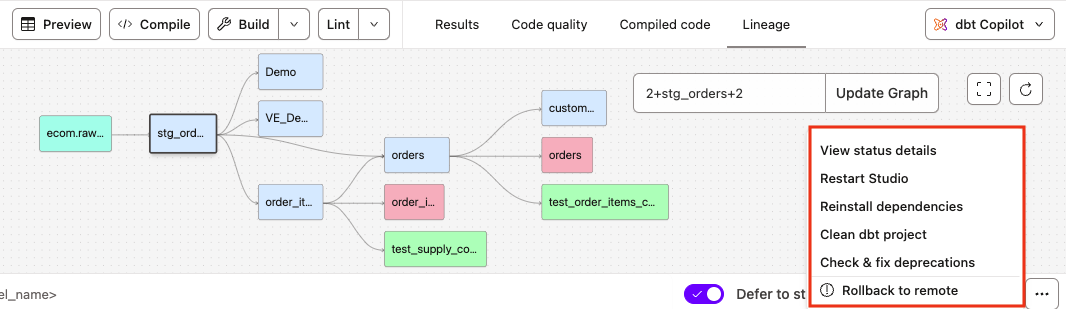
- Click the three-dot menu in the bottom right corner of the Studio IDE.
- Select Check & fix deprecations.
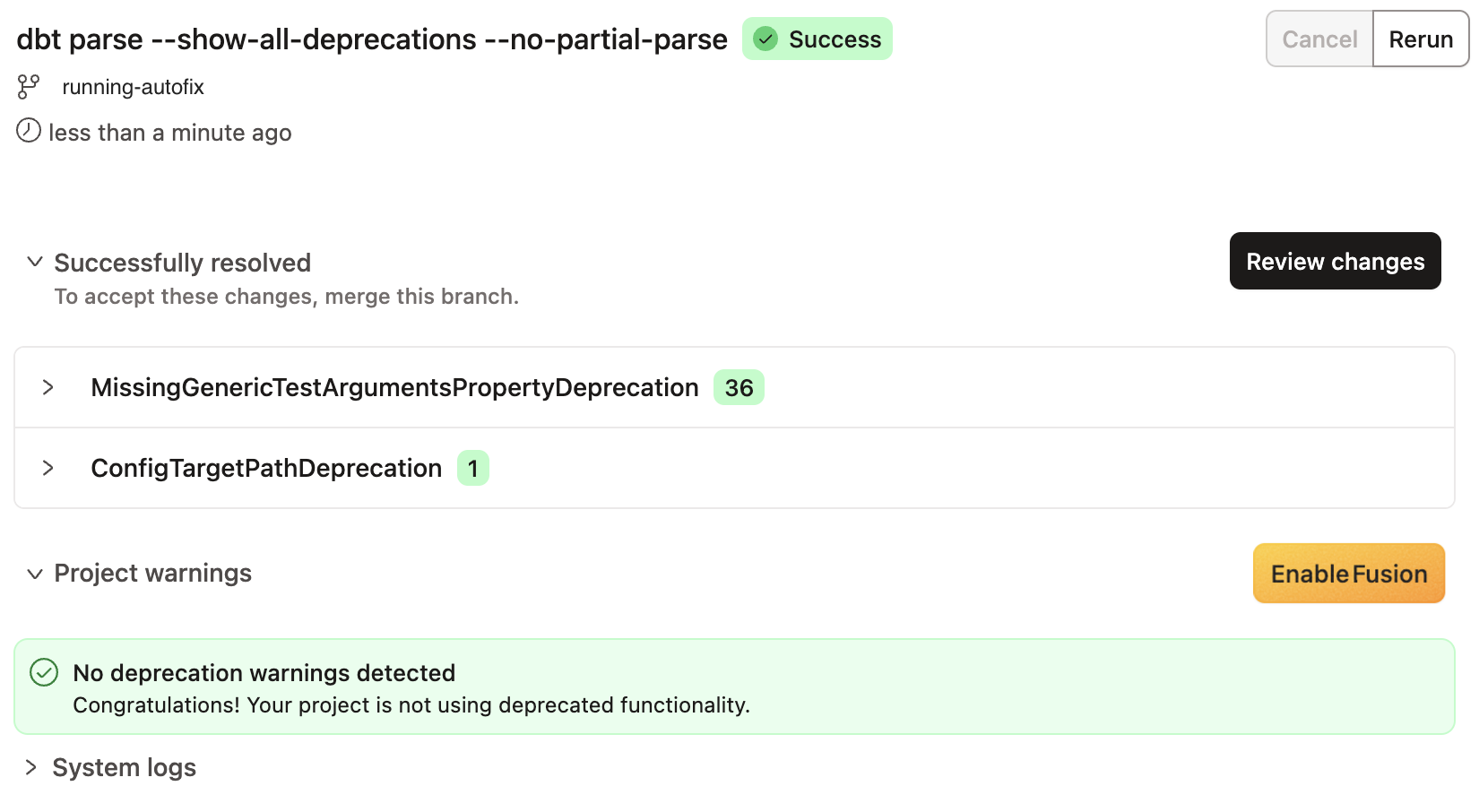
The tool runs dbt parse --show-all-deprecations --no-partial-parse to identify all deprecations in your project. This may take a few moments depending on your project size.
- When parsing completes, view the results in the Command history panel in the bottom left.
Step 3: Review and apply autofixes
After the deprecation scan completes, review the findings and apply automatic fixes:
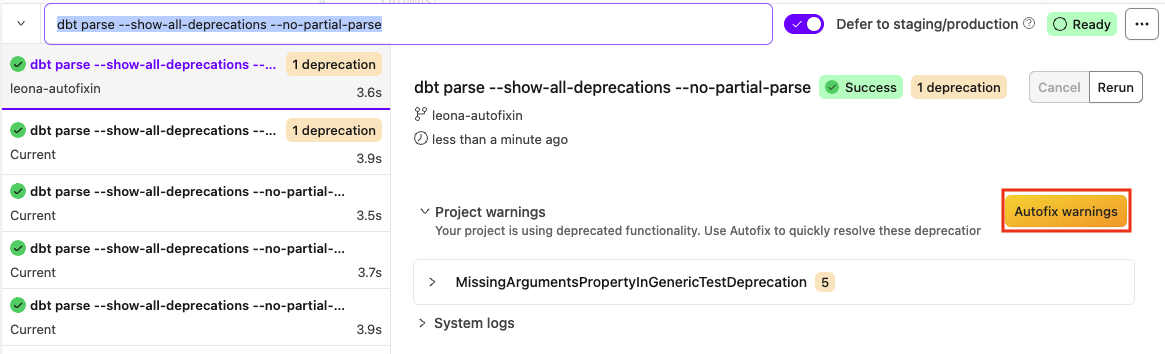
- In the Command history panel, review the list of deprecation warnings.
- Click the Autofix warnings button to proceed.
- In the Proceed with autofix dialog, review the warning and click Continue.
The tool automatically modifies your project files to resolve fixable deprecations, then runs another parse to identify any remaining warnings.
- When complete, a success message appears. Click Review changes.
Step 4: Verify the changes
Review the changes made by the autofix tool to ensure they're correct:
- Open the Version control panel to view all modified files.
- Click on individual files to review the specific changes.
- Look for files with moved configurations, corrected properties, or updated syntax.
- If needed, make any additional manual adjustments.
Step 5: Commit your changes
Once you're satisfied with the autofix changes, commit them to your branch:
- In the Version control panel, add a descriptive commit message like "Fix deprecation warnings for Fusion upgrade".
- Click Commit and sync to save your changes.
Step 6: Address remaining deprecations
If the autofix tool reports remaining deprecation warnings that couldn't be automatically fixed:
- Review the warning messages in the Command history panel — each warning includes the file path and line number.
- Manually update the code based on the deprecation guidance:
- Custom inputs should be moved to the
metaconfig. - Deprecated properties should be updated to their new equivalents.
- Refer to specific version upgrade guides for detailed migration instructions.
- Custom inputs should be moved to the
- After making manual fixes, run Check & fix deprecations again to verify all warnings are resolved.
- Commit your changes.
Step 7: Merge to your main branch
Once all deprecations are resolved:
- Create a pull request in your git provider to merge your deprecation fixes.
- Have your team review the changes.
- Merge the PR to your main development branch.
- Ensure these changes are deployed to your environments before proceeding with the Fusion upgrade.
Validate and upgrade your dbt packages
dbt packages extend your project's functionality, but they must be compatible with Fusion. Most commonly used packages from dbt Labs (like dbt_utils and dbt_project_evaluator) and many community packages already support Fusion. Before upgrading, verify your packages are compatible and upgrade them to the latest versions.
If a critical package isn't yet compatible with Fusion:
- Check with the package maintainer about their roadmap
- Open an issue requesting Fusion support
- Consider contributing the compatibility updates yourself
- Temporarily remove the package until it's compatible
Step 1: Review your current packages
Identify which packages your project uses:
- In the Studio IDE, open your project's root directory.
- Look for either
packages.ymlordependencies.ymlfile (both are valid, butdependencies.ymlis the newer format). - Review the list of packages and their current versions.
Your file will look something like this:
packages:
- package: dbt-labs/dbt_utils
version: 1.0.0
- package: dbt-labs/codegen
version: 0.9.0
Step 2: Check compatibility and find the latest package versions
Review the supported packages list to see verified Fusion-compatible packages.
For packages not on this list:
- Visit the package's GitHub repository.
- Check the README or recent releases for Fusion compatibility information.
- Look for issues or discussions about Fusion support.
For each package, find the most recent version:
- Visit dbt Hub for packages hosted there.
- For packages from GitHub, check the repository's releases page.
- Note the latest version number for each package you use.
For Hub packages, you can use version ranges to stay up-to-date:
packages:
- package: dbt-labs/dbt_utils
version: [">=1.0.0", "<2.0.0"] # Gets latest 1.x version
Step 3: Update your package versions
Update your packages.yml or dependencies.yml file with the latest compatible versions:
-
In the Studio IDE, open your
packages.ymlordependencies.ymlfile. -
Update each package version to the latest compatible version.
-
Save the file.
Before update:
packages:
- package: dbt-labs/dbt_utils
version: 0.9.6
- package: dbt-labs/codegen
version: 0.9.0After update:
packages:
- package: dbt-labs/dbt_utils
version: [">=1.0.0", "<2.0.0"]
- package: dbt-labs/codegen
version: [">=0.12.0", "<1.0.0"]
Step 4: Install updated packages
After updating your package versions, install them:
- In the Studio IDE command line, run:
dbt deps --upgrade
The --upgrade flag ensures dbt installs the latest versions within your specified ranges, updating the package-lock.yml file.
- Review the output to confirm all packages installed successfully.
- Check that the
package-lock.ymlfile was updated with the new package versions.
The package-lock.yml file pins your packages to specific versions for reproducible builds. We recommend committing this file to version control so your entire team uses the same package versions.
Step 5: Test your project with updated packages
After upgrading packages, test your project to ensure everything works:
-
Run a subset of your models to verify basic functionality:
dbt run --select tag:daily -
Run your tests to catch any breaking changes:
dbt test -
If you encounter issues:
- Review the package's changelog for breaking changes
- Adjust your code to match new package behavior
- If problems persist, temporarily pin to an older compatible version
Step 6: Commit package updates
Once you've verified the updated packages work correctly:
-
In the Version control panel, stage your changes:
packages.ymlordependencies.ymlpackage-lock.yml
-
Add a commit message like "Upgrade dbt packages for Fusion compatibility".
-
Click Commit and sync.
Check for known Fusion limitations
While Fusion supports most of dbt Core's capabilities, some features have limited support or are still in development. Before upgrading, review your project to identify any features that Fusion doesn't yet fully support. This allows you to plan accordingly — whether that means removing non-critical features, implementing workarounds, or waiting for specific features to become available.
Many limitations are being addressed as Fusion moves toward General Availability. You can track progress on specific features through the dbt-fusion GitHub milestones and stay updated via the Fusion Diaries.
Step 1: Review the limitations table
Start by understanding which features have limited or no support in Fusion:
Visit the Fusion supported features page and review the limitations table to see features that may affect your project.
Common limitations include:
- Python models: Not currently supported (Fusion cannot parse Python to extract dependencies)
- Microbatch incremental strategy: Not yet available
- Model-level notifications: Job-level notifications work, model-level don't yet
- Semantic Layer development: Active semantic model development should stay on dbt Core
- SQLFluff linting — Not integrated yet (though linting will be built into Fusion directly)
Step 2: Search your project for limited features
Check if your project uses any features with limited support:
-
Check for Python models:
- In the Studio IDE, look in your
models/directory - Search for files with
.pyextensions - If found, you'll need to either remove them or keep those models on dbt Core
- In the Studio IDE, look in your
-
Review your
dbt_project.ymlfor specific configurations:- Look for
store_failuressettings - Check for custom materializations beyond
view,table, andincremental - Review any
warn-errororwarn-error-optionsconfigurations
- Look for
-
Check your job configurations:
- Review any jobs using
--fail-fastflag - Identify jobs using
--store-failures - Note any Advanced CI "compare changes" workflows
- Review any jobs using
-
Review model governance settings:
- Search for models with
deprecation_dateset - Note these may not generate deprecation warnings yet in Fusion
- Search for models with
Step 3: Assess the impact
For each limitation that affects your project, determine its criticality:
-
Critical features: Features your project can't function without:
- If Python models are essential, you may need to wait or refactor them to SQL
- If Semantic Layer development is active, continue those workloads on dbt Core
-
Nice-to-have features: Features that improve workflows but aren't blockers:
- Model-level notifications can be replaced with job-level notifications temporarily
- SQLFluff linting can continue running with dbt Core in CI
-
Minimal impact: Features you can easily work around:
--fail-fastcan be removed from job commands--store-failurescan be disabled temporarily
Step 4: Create an action plan
Based on your assessment, decide how to handle each limitation:
-
Remove non-critical features:
Temporarily disable features you can live without:
# Before (in model config)
{{ config(
materialized='incremental',
store_failures=true
) }}
# After
{{ config(
materialized='incremental'
) }} -
Implement workarounds for low-impact features.
- Use job-level notifications instead of model-level
- Run SQLFluff linting separately in CI with dbt Core
- Use standard state selection instead of granular subselectors
-
Plan hybrid environments for critical unsupported features.
- Keep specific jobs on dbt Core (like Semantic Layer exports)
- Migrate development and most production workloads to Fusion
- Document which jobs need to remain on dbt Core and why
Step 5: Document your findings
Create a record of limitations affecting your project:
-
In your Studio IDE, create a document (like
FUSION_MIGRATION.md) listing:- Features your project uses that Fusion doesn't fully support
- Which models or jobs are affected
- Your mitigation strategy for each limitation
- GitHub issue links to track when features become available
-
It's critical that your teams understand the limitations so share this document with your stakeholders.
Step 6: Track feature progress
Stay up-to-date with feature availability:
- Subscribe to relevant GitHub issues for features you need (linked in the limitations table).
- Follow the Fusion Diaries for updates.
- Check the dbt-fusion milestones to see release timelines.
What's next?
With limitations identified and addressed, you've completed all the preparation steps. Your project is now ready to upgrade to Fusion!
Check out Part 2: Making the move
Was this page helpful?
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.